Popular Science Presentations
How does the expression of the genes affect all the different functions of the entire organism?
In physiology, we investigate with the help of physiological, biochemical and molecular studies how different animals and plants have adapted to different lifestyles and habitats. We study whole organisms as well as animals and plants at the tissue, cell and molecular level. An important question is how different physiological processes have developed from a more primitive stage to a more advanced and complex form, as well as what changes have taken place during the course of development.
What historical factors and genetic mechanisms are behind vertebrate diversity?
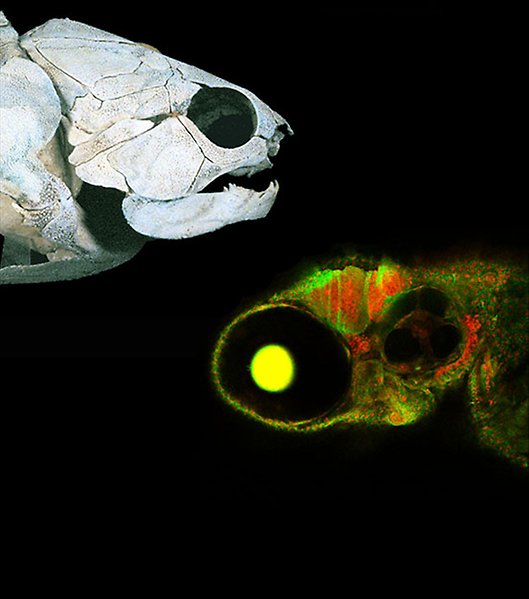
In the department of Evolution andDevelopmental Biology, we study how the body shape, internal structure and function of different vertebrates have been changed during evolution. We use information from fossils and living animals, and also investigate the underlying developmental biological and genetic processes that give rise to the diversity we see in vertebrates today. Of particular interest is reconstructing the order in which character traits have arisen over time. By linking this to how the expression of genes affects the development from embryo to adult individual, we can better understand the evolutionary history of vertebrates.
How do chemicals found in the environment affect different functions in animals and humans?
Within Environmental Toxicology, we study how chemicals used in different parts of the society affect physiological functions such as for example reproduction and behavior. In several experimental animal models, we study, among other things, how exposure to chemicals early in development can produce effects later in life. Of particular interest is clarifying how the chemicals work at the molecular and cellular level. Our animal models include fish, frogs, birds and rodents.
How did the modern human came to be?
In Human Evolution, we study how the modern human has evolved, its history and genetics. We can use current genetic methods to analyse ancient gentic material from prehistoric humans and compare it to material from today's humans, and in this way find out how humans have spread across the world and how human genetics have changed. Using this, we can find knowledge about humanity's hidden past.
What does biological diversity look like and how was it created?
Humans have tried to find out what kind of species there are and why we see patterns in the diversity since before the time of Carl Linnaeus, in the 18th century. In the 19th century, Darwin presented his theory of evolution and provided a scientific explanation for these patterns. The more we learn about biodiversity, the more we understand how massive it is, likely more than 9 million species where the vast majority are still not scientifically described. We study biological diversity and the evolutionary processes which creates it at Systematic Biology. We study diversity both within and between organisms. This includes describing new species but also using novel technologies to study the hidden diversity. Our research covers many types of eukaryotes, from unicellular microorganisms to animals, fungi and plants.